- Published on
Building GitOps CI/CD Pipeline for Kustomize Application using GitHub Actions
- Authors
- Name
- Geonhyuk Im
- @GeonHyuk
Building GitOps CI/CD Pipeline for Kustomize Application using GitHub Actions
In this blog post, I will demonstrate how I built a cross-repository GitOps CI/CD pipeline for Kustomize application leveraging GitHub Actions Reusable workflow and Cross-repository GitOps pattern.
Table of Contents
- Workflow Architecture and Design
- Implementation Details
- Common Issues and Solutions
Workflow Architecture and Design
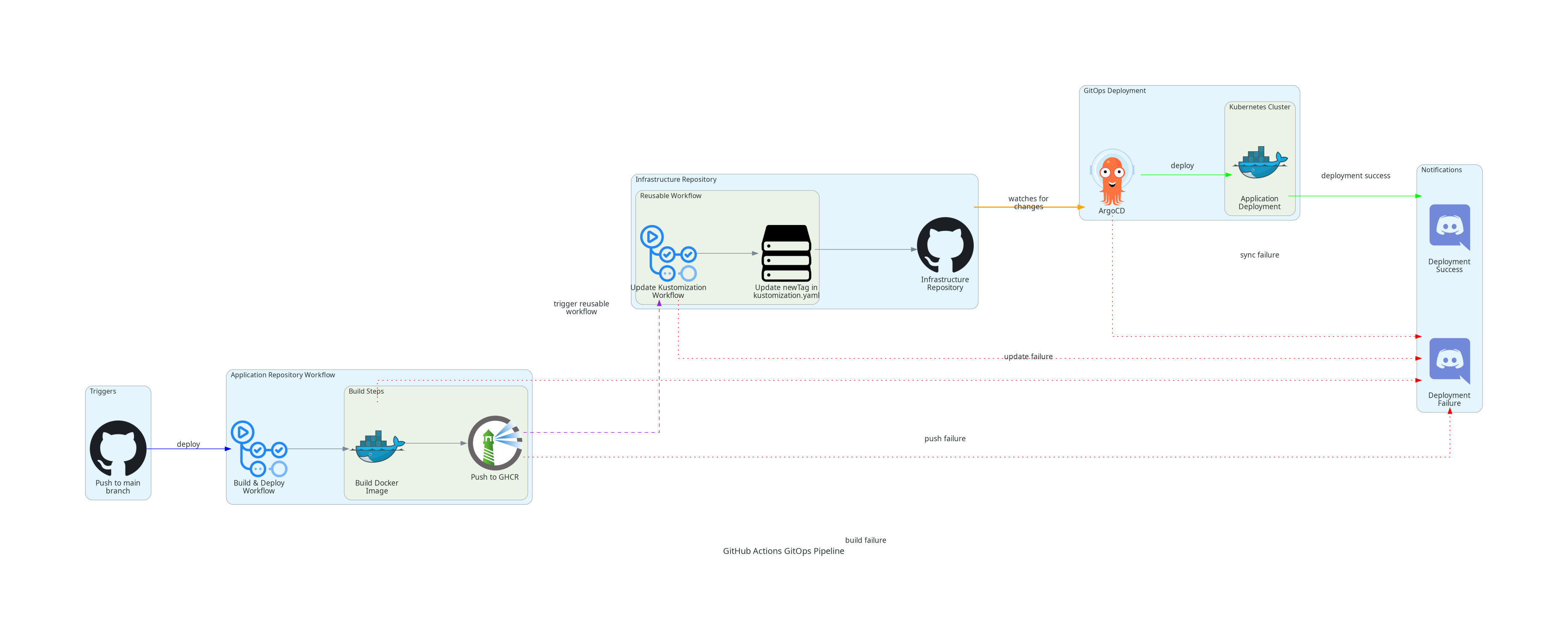
When application repository pushes to the main branch, the workflow will be triggered. The application repository workflow will build the Docker image and push it to GitHub Container Registry. After the CI phase, the workflow triggers another workflow in the infrastructure repository to update the kustomization.yaml file with the new image tag.
Finally, ArgoCD detects the updated kustomization.yaml and deploys the new image to the cluster, completing the CD phase.
Implementation Details
I will share the implementation details of the pipeline, step by step in the following sections. I assume that you already have ArgoCD deployed and the ArgoCD authentication to infrastructure repository is configured.
For my case, I structured the GitOps repository in the following way:
Infrastructure Repository:
.
├── apps
│ ├── {app-name}
│ │ base
│ │ overlays
│ │ ├── {environnment} (e.g. dev, qa, staging, prod)
│ │
Step 1: Configure GitHub App and Repository Secrets for Cross-Repository Authentication
For calling reusable workflow in another repository, we need to configure GitHub App and GitHub Actiosn secrets in both application and infrastructure repositories.
GitHub App Configuration
First, we need to create a GitHub App in GitHub account and install it in the application and infrastructure repositories. This step applies to both personal and organization accounts. We need to create a GitHub App with the following permissions:
- Actions: Read and write
- Contents: Read and write
In GitHub settings page, go to Developer settings -> GitHub Apps -> and create New GitHub App or edit existing GitHub App. 
GitHub App needs permissions to access the repository. Make sure Actions: Read and Write and Contents: Read and Write are checked. 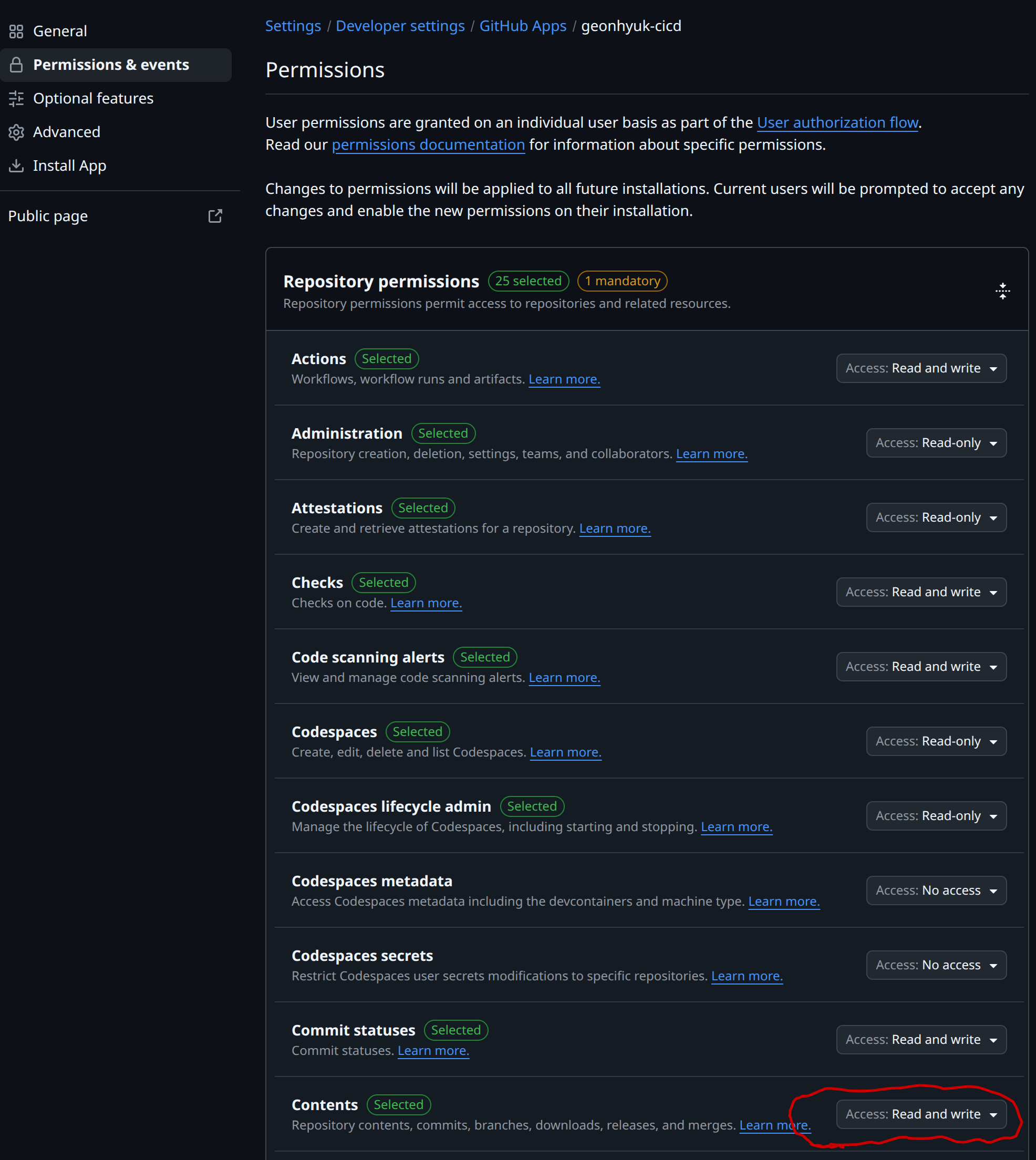
After creating the GitHub App, Settings -> Integrations -> Applications, and make sure the GitHub App is installed in the account and access to the repository is granted.
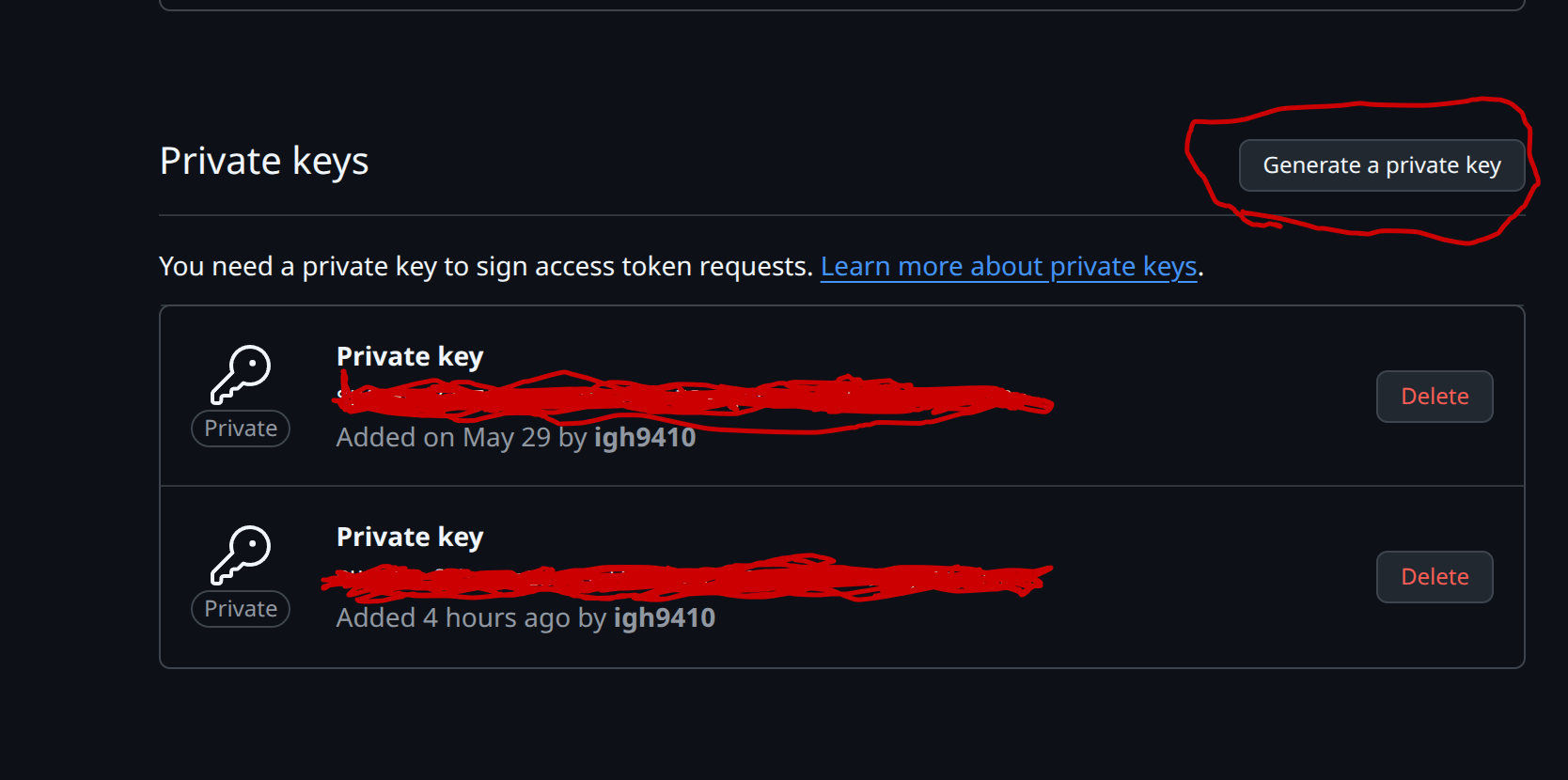
GitHub Actions Secrets Configuration GitHub App id and private key are required for cross-repository authentication. You can find the GitHub App id and generate private key in the GitHub App settings page. 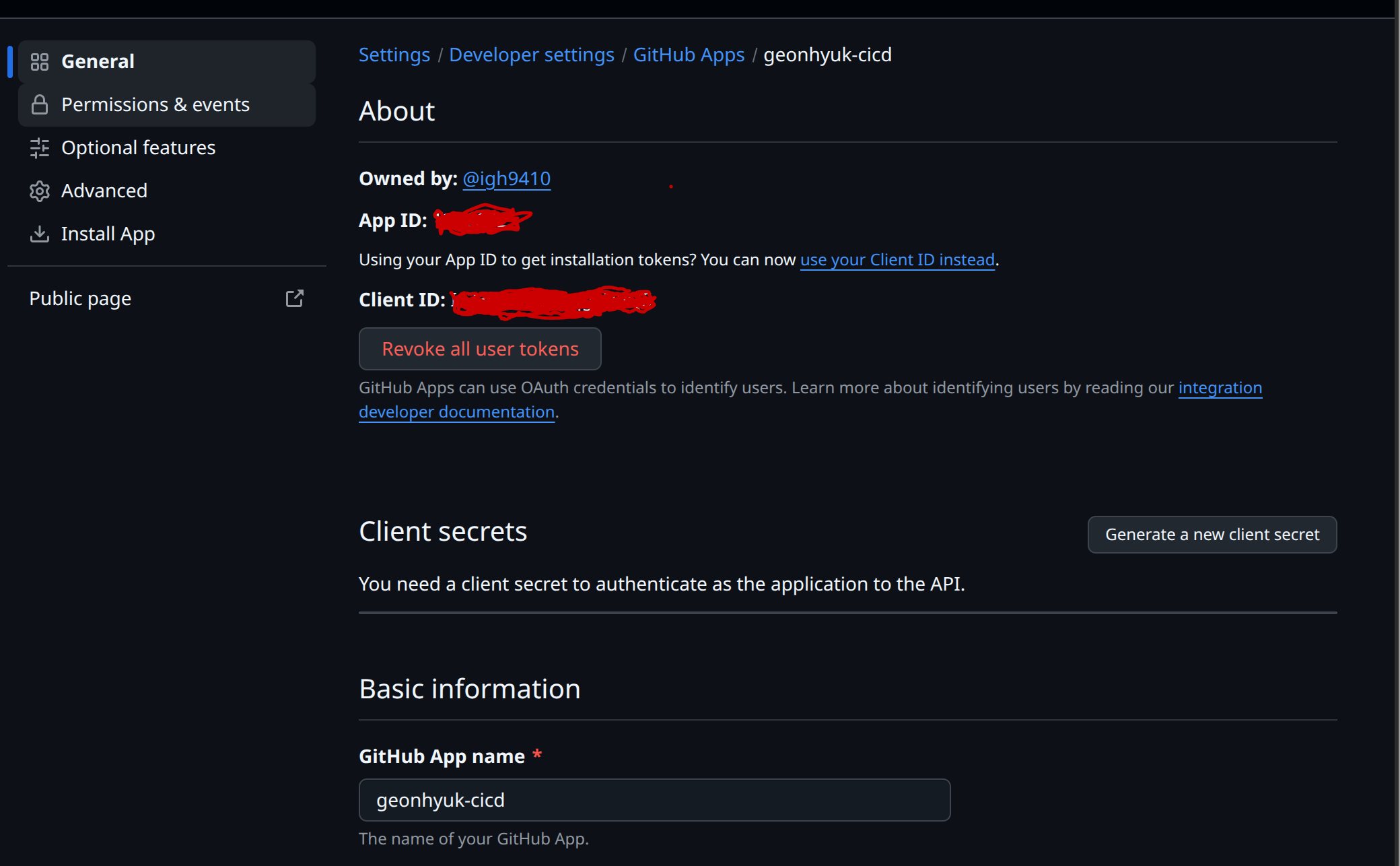
We need to create GitHub Actions secrets in both application and infrastructure repositories. 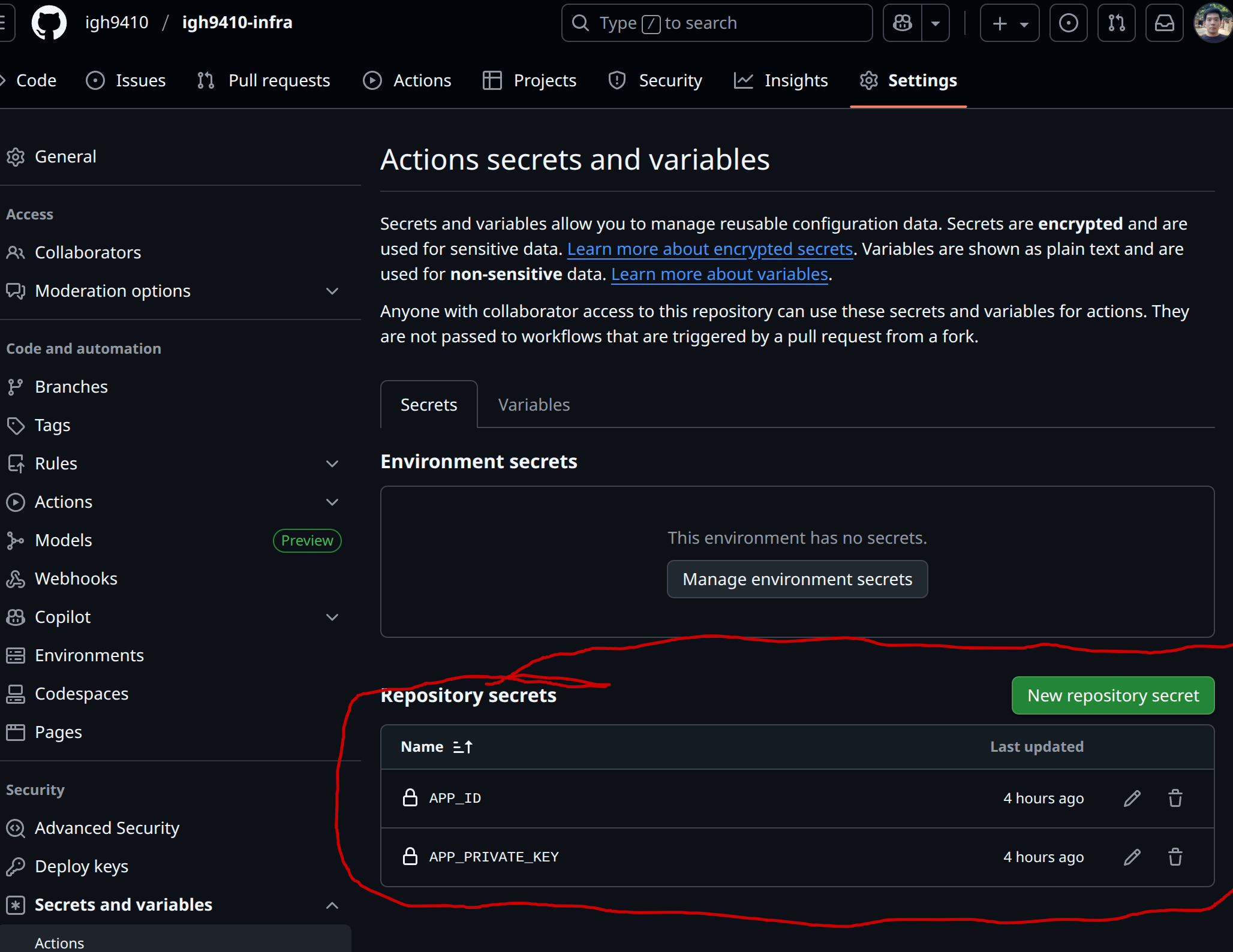
In both repositories, configure secrets with the following names and values:
APP_ID: GitHub App idAPP_PRIVATE_KEY: GitHub App private key (the value of .pem file)
Step 2: Create Reusable Workflow
I created a reusable workflow in my infrastructure repository and committed it to the main branch.
name: Deploy Kustomize App
on:
workflow_call:
inputs:
app_name:
description: 'Application to deploy'
required: true
type: string
environment:
description: 'Environment to deploy (e.g., dev, qa, staging, prod)'
required: true
type: string
commit_sha:
description: 'Commit SHA to update the image tag to'
required: true
type: string
secrets:
APP_ID:
description: 'GitHub App ID'
required: true
APP_PRIVATE_KEY:
description: 'GitHub App Private Key'
required: true
permissions:
contents: write
jobs:
kustomize-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Generate GitHub App Token
uses: actions/create-github-app-token@v2
id: app-token
with:
app-id: ${{ secrets.APP_ID }}
private-key: ${{ secrets.APP_PRIVATE_KEY }}
owner: igh9410
repositories: igh9410-infra
- name: Checkout Infrastructure Repo
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
repository: igh9410/igh9410-infra
ref: main
token: ${{ steps.app-token.outputs.token }}
path: igh9410-infra
- name: Update kustomization.yaml
working-directory: igh9410-infra
env:
FILE: 'apps/${{ inputs.app_name }}/overlays/${{ inputs.environment }}/kustomization.yaml'
run: |
echo "Updating $FILE with commit SHA ${{ inputs.commit_sha }}"
yq -i '.images[0].newTag = "${{ inputs.commit_sha }}"' "$FILE"
- name: Commit and push changes
working-directory: igh9410-infra
run: |
git config --global user.name '${{ steps.app-token.outputs.app-slug }}[bot]'
git config --global user.email '${{ steps.get-user-id.outputs.user-id }}+${{ steps.app-token.outputs.app-slug }}[bot]@users.noreply.github.com'
git add apps/${{ inputs.app_name }}/overlays/${{ inputs.environment }}/kustomization.yaml
git commit -m "chore: update ${{ inputs.app_name }} image to ${{ inputs.commit_sha }}"
git push origin main
And configure the infrastructure repository's settings to allow a reusable workflow to be called from the application repository. 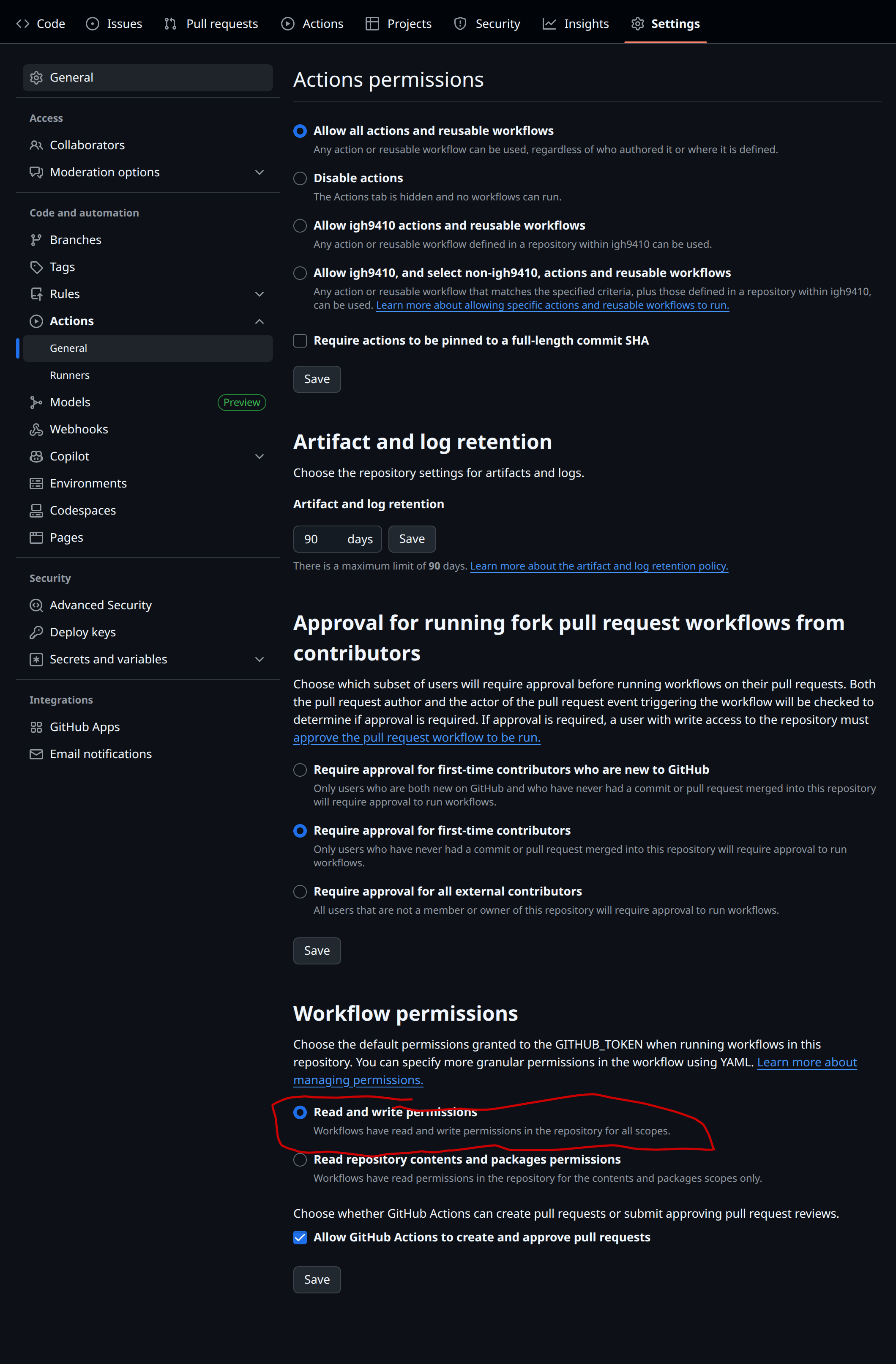
Step 3: Calling Reusable Workflow from Application Repository's Workflow
In application repository, the reusable workflow can be called like below:
name: Build and Deploy with ArgoCD
on:
# Automatic trigger on push to main
push:
branches: [main]
paths-ignore:
- 'apps/*' # frontend apps
- 'packages/*' # frontend packages
permissions:
contents: write # Required for checkout and pushing changes
packages: write # Required for publishing packages to GHCR
id-token: write # Required for OIDC authentication
jobs:
build-and-push:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ needs.determine-environment.outputs.target_ref }}
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
- name: Log in to GitHub Container Registry
uses: docker/login-action@v3
with:
registry: ghcr.io
username: ${{ github.repository_owner }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Build and push Docker image
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
with:
push: true
tags: |
ghcr.io/${{ github.repository_owner }}/gramnuri-api:${{ github.sha }}
update-image-tag:
needs: [build-and-push]
uses: igh9410/igh9410-infra/.github/workflows/deploy-kustomize-app.yaml@main
with:
app_name: app-name (the name of the application)
environment: 'dev' # or "staging", "qa", "prod"
commit_sha: '${{ github.sha }}' # The commit SHA of application repository
secrets:
APP_ID: ${{ secrets.APP_ID }}
APP_PRIVATE_KEY: ${{ secrets.APP_PRIVATE_KEY }}
needs: [build-and-push] ensures that the updating image tag in infra repo called after the build-and-push job is completed.
Application repository workflow screenshot: 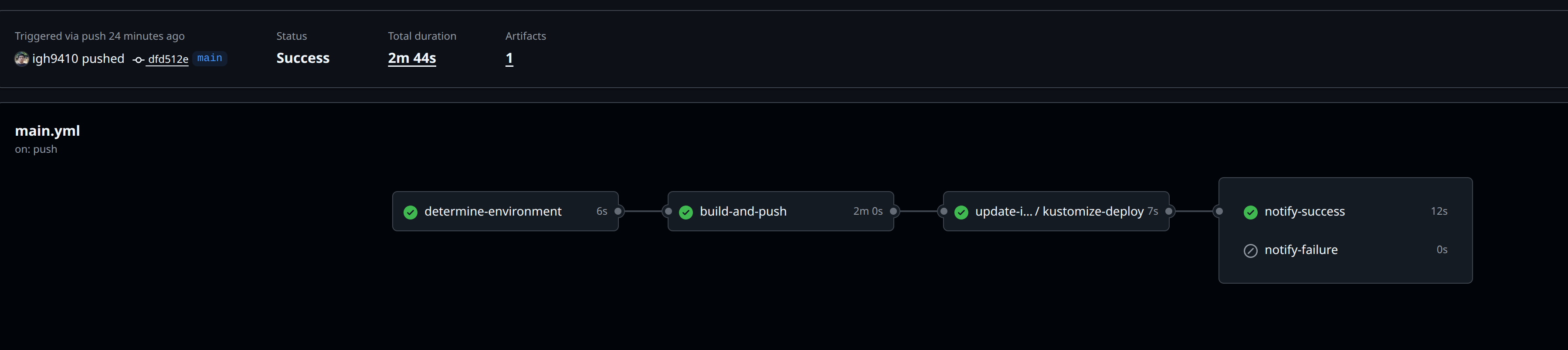
And new commit is pushed to the infrastructure repository made by GitHub Actions: 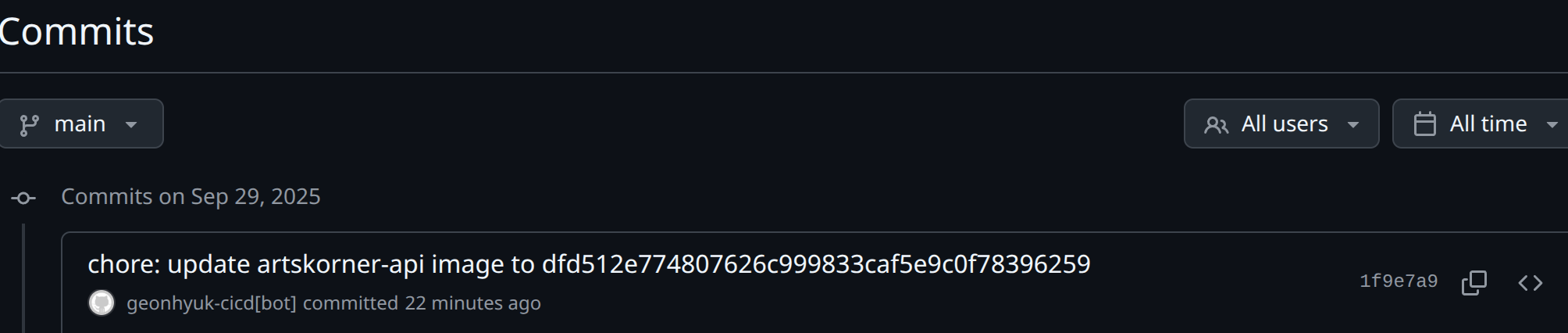
Finally, ArgoCD detected the new commit and deployed the new image to the cluster: 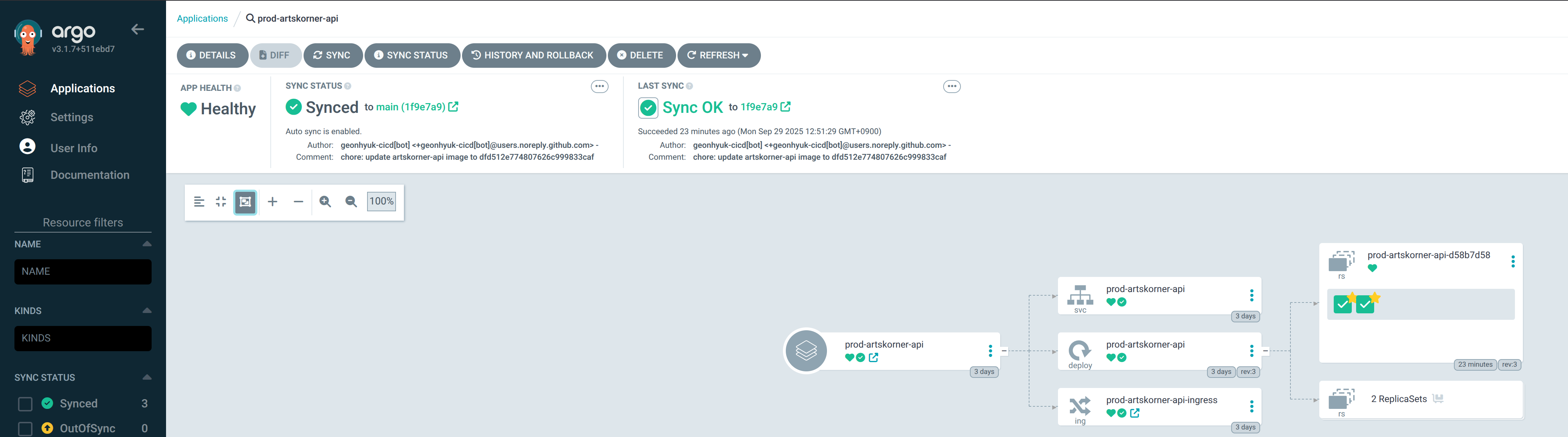
Common Issues and Solutions
Permission Denied Error
- If you encounter a permission denied error, make sure the GitHub App is installed in the application and infrastructure repositories.
- Check if the GitHub App has the read-and-write permissions for contents and actions to access the repository.
- Make sure the GitHub Actions secrets are configured correctly for both repositories.
- The infrastructure repository's settings page should allow a reusable workflow to be called from the application repository and workflow permissions should have read and write permissions.
Conclusion
In this blog post, I demonstrated how I built a modularized, secure cross-repository GitOps CI/CD pipeline. This pipeline is modularized and can be reused for other applications without code duplication.
Also, since this uses GitHub App's token, not the Personal Access Token, it is more secure and reliable for long-term production use. You can find the complete infrastructure code in my GitHub repository.