- Published on
✨ Streamlined ECS CI/CD Pipeline with GitHub Actions and Multi-Environment Deployment
- Authors
- Name
- Geonhyuk Im
- @GeonHyuk
Streamlined ECS CI/CD Pipeline with GitHub Actions and Multi-Environment Deployment
Modern software development requires efficient, reliable deployment pipelines that can handle multiple environments while maintaining appropriate controls. Here's how I designed a comprehensive CI/CD pipeline for AWS ECS using GitHub Actions that supports different deployment strategies for each environment.
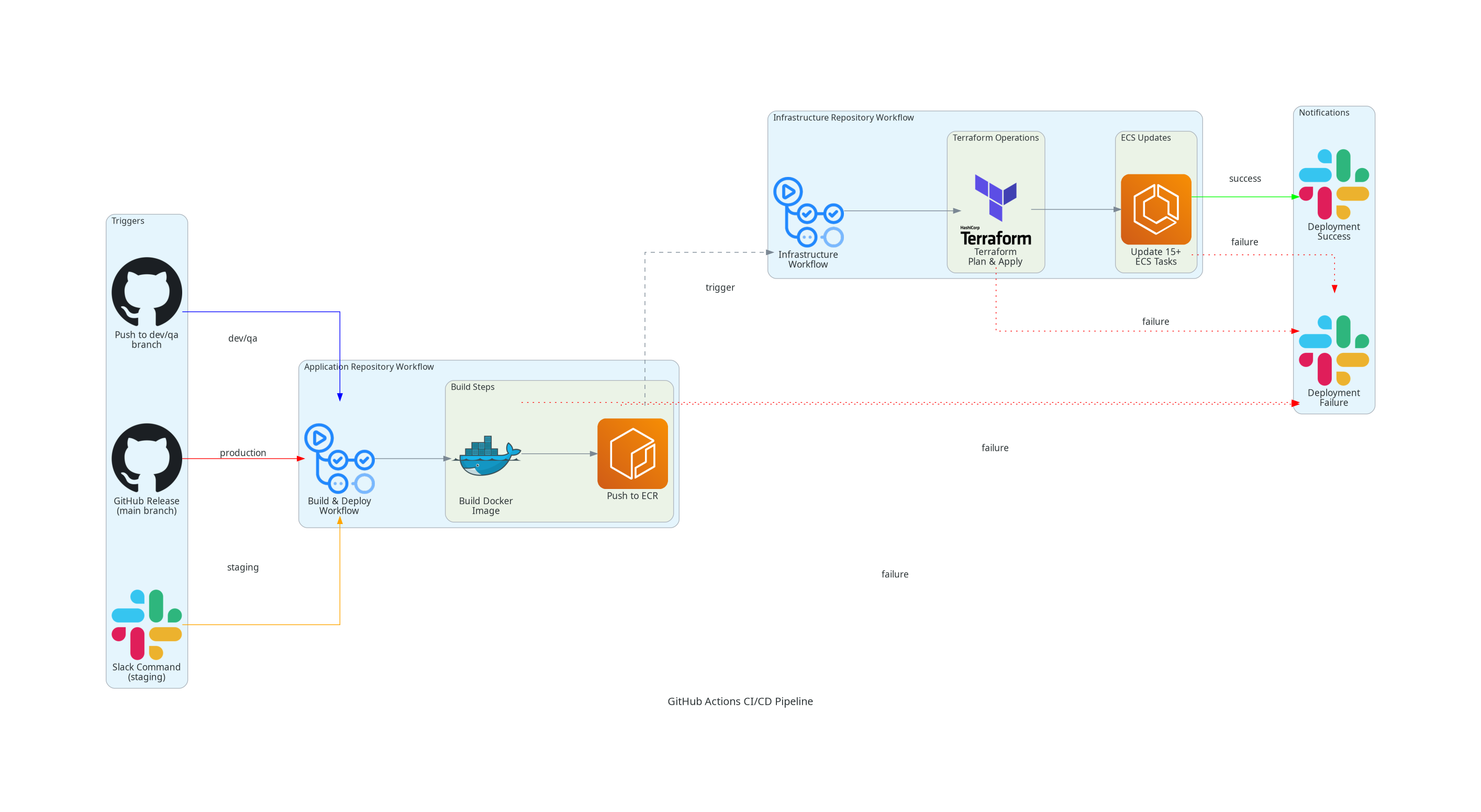
Pipeline Architecture Overview
The pipeline follows a two-repository approach where the application repository handles building and the infrastructure repository manages deployments. This separation of concerns ensures better security and maintainability.
Multi-Trigger Strategy
Different environments use different deployment triggers to balance automation with control:
Development & QA Environments
Trigger: Automatic on code push to dev or qa branches
When developers push code to development or QA branches, the pipeline automatically:
- Builds the Docker image
- Pushes to Amazon ECR
- Triggers infrastructure deployment
- Updates 15+ ECS scheduled tasks
- Sends success/failure notifications to Slack
This immediate feedback loop enables rapid development iteration and testing.
Production Environment
Trigger: GitHub Release creation
Production deployments require deliberate action through GitHub releases:
- Creates a formal release record
- Ensures production deployments are intentional
- Provides clear versioning and release notes
- Follows the same build and deployment process as other environments
Staging Environment
Trigger: ChatOps via Slack commands
Staging deployments can be triggered on-demand through Slack:
- Uses the latest commit from the QA branch
- Slack cha
- Provides flexible deployment timing
- Supports collaborative testing workflows
Key Benefits
Environment-Appropriate Controls
Each environment has deployment triggers that match its purpose - automation for dev/QA, formal releases for production, and on-demand access for staging.
Automated Infrastructure Management
The pipeline automatically manages infrastructure changes through Terraform, ensuring consistency across deployments and reducing manual configuration drift.
Comprehensive Notifications
Slack integration provides immediate feedback on deployment status, keeping teams informed about successful deployments and failures requiring attention.
Separation of Concerns
By splitting application builds and infrastructure deployments across repositories, the pipeline maintains clear boundaries between application code and infrastructure configuration.
Workflow Process
- Build Phase: Application repository builds Docker images and pushes to ECR
- Deploy Phase: Infrastructure repository applies Terraform changes and updates ECS tasks
- Notification Phase: Teams receive deployment status updates via Slack
The pipeline includes failure handling at each step, ensuring teams are notified immediately when issues occur during build, infrastructure deployment, or ECS task updates.
Conclusion
This CI/CD architecture provides the right balance of automation and control for different environments. Development teams get rapid feedback, production deployments remain controlled and traceable, and staging environments offer flexible testing capabilities through ChatOps integration.
The combination of GitHub Actions, Terraform automation, and comprehensive notifications creates a robust deployment pipeline that scales with team needs while maintaining reliability and visibility across all environments.